Non-performing assets (NPAs) are loans or advances that fail to generate income for banks, either due to borrowers defaulting intentionally or being unable to repay because of economic downturns affecting their business. This situation can lead to partial or complete non-recovery of the loan, reflecting negatively on a bank’s ability to efficiently manage deposits and loan recovery. The consequences include a decrease in interest income, higher provisions for NPAs, increased capital requirements, and diminished profits. Addressing the impact of NPA on banks is crucial for banks to maintain their financial health and operational efficiency. Debt settlement can be a cost-effective escape from high-interest debt, negotiating lower amounts you owe, though fees for these services might reduce your overall savings. As a result, to learn more about debt relief strategies for settlement, click the link right now!
Understanding the Impact of NPA on Banks: A Deep Dive
In the intricate world of banking and finance, Non-Performing Assets (NPAs) stand as a formidable challenge, affecting the liquidity, profitability, and operational efficiency of banking institutions. The impact of NPA on banks cannot be overstated, as it directly correlates with the financial health and sustainability of these institutions. Through a detailed exploration, this article aims to shed light on the multifaceted effects of NPAs and the strategies banks can employ to mitigate these challenges.
The Economic Repercussions of Rising NPAs
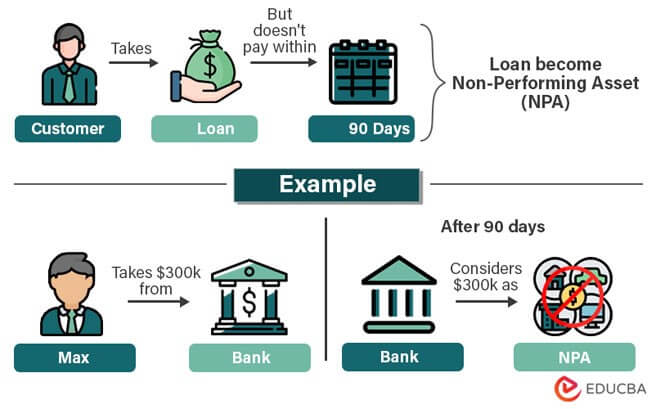
NPAs represent loans or advances that have ceased generating income for banks, either due to default in repayment or the erosion of the principal value of the loan. The rise in NPAs not only erodes the asset quality of banks but also diminishes their income streams, leading to a direct impact on their profitability margins. This situation necessitates increased provisioning for NPAs, further straining the banks’ net interest margins (NIMs) and overall financial health.
Operational Challenges and Strategic Diligence
The operational challenges posed by high levels of NPAs are manifold. Banks find themselves in a precarious position, having to balance between making adequate provisions for NPAs and maintaining sufficient capital adequacy ratios as per regulatory requirements. This balancing act requires strategic diligence and a proactive approach to asset quality management, emphasising the importance of robust risk assessment frameworks and early warning systems.
Mitigating the Impact through Strategic Interventions

To counteract the adverse effects of NPAs, banks have adopted various strategic interventions. These include the restructuring of loans, the implementation of asset reconstruction companies (ARCs), and the utilisation of strategic debt restructuring (SDR) mechanisms. Additionally, banks are increasingly focusing on strengthening their recovery mechanisms, employing legal and financial tools to expedite the recovery of dues from defaulting borrowers.
Innovative Approaches to NPA Management
In the era of digital transformation, banks are leveraging technology to enhance their NPA management strategies. Advanced analytics and machine learning algorithms are being deployed to predict potential NPAs, enabling banks to take preemptive measures. Furthermore, digital platforms facilitate streamlined and efficient recovery processes, improving the speed and effectiveness of NPA resolutions.
Regulatory Frameworks and Policy Support
The regulatory landscape plays a pivotal role in shaping the banks’ approach to managing NPAs. Regulatory bodies have introduced various frameworks and guidelines aimed at minimising the creation of new NPAs and facilitating the resolution of existing ones. Policy measures such as the Insolvency and Bankruptcy Code (IBC) have been instrumental in providing a structured approach to NPA resolution, ensuring timely recovery, and minimising the financial impact on banks.
The Path Forward: Resilience and Adaptation
The journey towards minimising the impact of NPAs on banks is ongoing and requires continuous adaptation and resilience. Banks must remain vigilant, enhancing their credit monitoring and risk management practices to prevent the formation of new NPAs. Simultaneously, the adoption of innovative solutions and the effective implementation of regulatory frameworks will be key to navigating the challenges posed by NPAs.
FAQs (Frequently Asked Questions)
1. What is the definition of an NPA (non-performing asset)?
An NPA is a loan or advance where the principal or interest payment remains overdue for 90 days or more.
2. How does the NPA affect the profitability of banks?
NPAs impact bank profitability by:
Reducing interest income
Increasing provisioning expenses
Eroding capital base
3. What are the key factors contributing to NPA growth in banks?
The primary factors driving NPA growth include:
Economic slowdown
Sub-optimal lending practices
Structural weaknesses in specific sectors
Diversion of funds
4. What steps are taken by the banks to address the NPA problem?
Banks employ various strategies to manage NPAs, such as:
Early detection and restructuring of loans
Recovery through legal proceedings
Sale of NPAs to asset reconstruction companies
Securitization of loans


Leave A Comment